
The January jobs report was far stronger than had been predicted, with the financial system including 517,000 jobs. There was additionally a giant enhance within the size of the typical workweek from 34.4 hours to 34.7 hours, which led to a rare 1.2 p.c rise within the index of mixture hours. The common hourly wage elevated by 10 cents, bringing the annual enhance during the last three months to 4.6 p.c. The general unemployment price fell to three.4 p.c, the bottom degree since 1969.
The prior two months’ information was additionally revised up by 71,000. This introduced the typical achieve during the last three months to 356,000 jobs.
The soar within the size of the typical workweek might have been affected by seasonal components. The unadjusted workweek ordinarily drops in January, however it truly rose by 0.2 hours this 12 months. That could possibly be partly attributable to raised than regular climate for the reference week. Additionally, the reported declines of 0.1 hour in every of the prior two months might have overstated the true drop.
Job Progress Was Widespread Throughout Industries
Nearly all sectors reported job beneficial properties in January. Building and manufacturing, that are normally the sectors most delicate to rate of interest hikes, added 25,000 and 19,000 jobs, respectively. Even residential development added 5,500 jobs. Employment in development is now up 3.6 p.c from pre-pandemic ranges, whereas manufacturing is up 1.7 p.c.
Eating places and well being care have been the 2 greatest job gainers, including 98,600 jobs and 58,200 jobs, respectively. Employment in well being care is now 1.1 p.c above its pre-pandemic degree, whereas restaurant jobs are nonetheless down by 1.3 p.c. Lodges added 14,800 jobs, however employment within the sector remains to be down by 11.9 p.c from February of 2020. Retail added 30,100 jobs, placing employment 0.2 p.c beneath the pre-pandemic degree.
Sectors Struggling to Get Staff Added Jobs
Nursing houses and baby care facilities had been having bother getting employees within the tight labor market, however each added a modest variety of jobs in January. Nursing houses added 4,500 jobs, leaving employment 13 p.c beneath its pre-pandemic degree, whereas baby care added 7,100 jobs, placing employment 5.5 p.c beneath the pre-pandemic degree.
State governments added 39,000 jobs in January, whereas native governments added 30,000. Employment within the sectors remains to be down by 3.8 p.c and a couple of.1 p.c, respectively, from pre-pandemic ranges.
Labor Drive Participation Measures Unchanged After Adjusting for Inhabitants Controls
The January information confirmed a 0.1 share level rise in each the labor drive participation price and the employment inhabitants ratio, however each have been attributable to new inhabitants controls within the family survey. After adjusting for the brand new inhabitants controls, each have been unchanged from their December degree.
Nonetheless, the inhabitants controls did considerably change the family survey’s total image during the last 12 months. With the brand new controls, the survey now reveals employment elevated by 2,760,000 from January of 2022 to January of 2023, with the brand new controls rising employment by 810,000.
Nevertheless, there have been additionally upward revisions to the institution survey with the brand new benchmark for March 2022 being integrated. This survey now reveals a achieve of 4,967,000 from January of 2022, which leaves a very giant hole of two.2 million. The family survey confirmed employment development of simply 84,000 in January, after adjusting for the controls, so it continues to offer a radically totally different image of the financial system.
Prime-Age Labor Drive Participation Price Nonetheless Under Pre-Pandemic Stage
With the brand new inhabitants controls, prime-age (25 to 54) labor drive participation is down 0.4 share factors from its pre-pandemic peak total, with a drop of 0.9 share factors for males, and 0.1 share factors for girls. The drop in male LFPR from pre-pandemic degree is largest for the 35-44 age group, down 2 share factors from the pre-pandemic peak. However, if we evaluate to the 2000 peak, the drop for the 35-44 group is 3.7 share factors, whereas the drop for the 25-34 age group is 5.2 share factors.
Share of Unemployment As a consequence of Job Leavers Rises
The share of unemployment attributable to voluntary quits rose to fifteen.3 p.c in January. That is 0.1 share factors larger than the 2000 peak, and 0.2 share factors larger than the 2019 peak, however beneath ranges hit within the fall.
Going within the different path, the period measures of unemployment all confirmed will increase in January. The common period elevated from 19.5 weeks to twenty.4 weeks, the median rose from 8.9 weeks to 9.1 weeks, whereas the share of long-term unemployed (greater than 26 weeks) elevated from 18.5 p.c to 19.4 p.c.
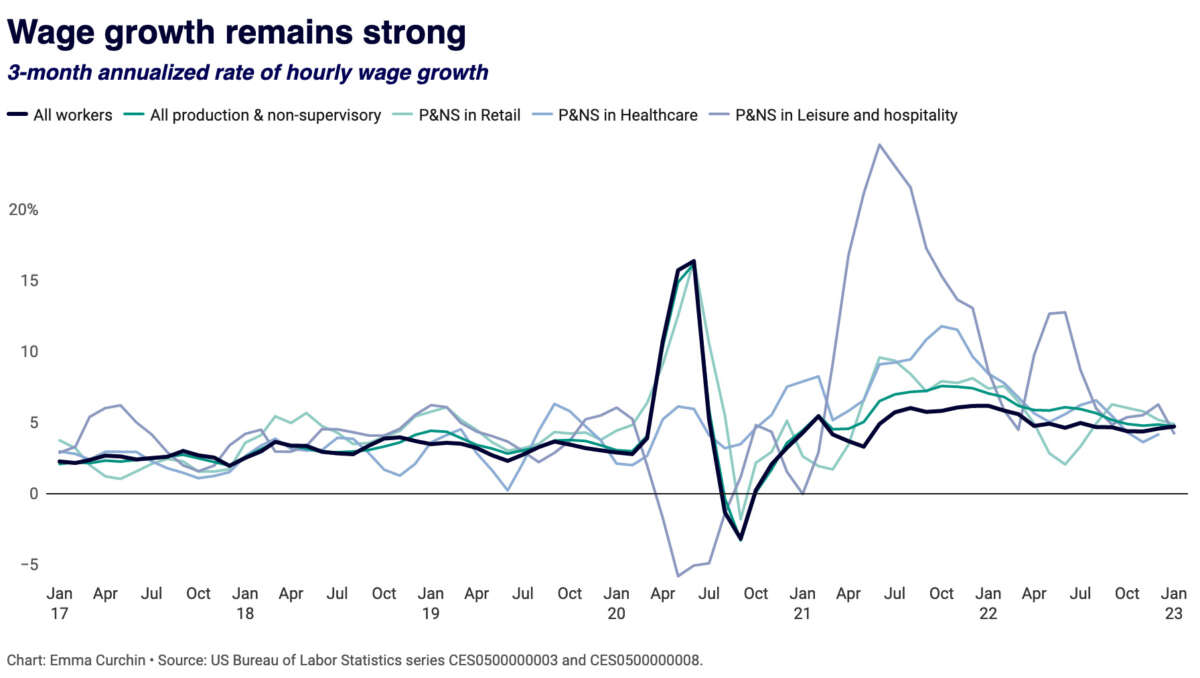
Combined Story on Wage Progress
The December information had indicated that the hourly wage was slowing to a tempo that was arguably in keeping with the Fed’s 2.0 p.c inflation goal. Whereas the December development was a modest 0.3 p.c, the annualized price over the prior three months is 4.6 p.c. That is probably quicker than could be in keeping with the Fed’s goal.
Nevertheless, the January determine is probably going considerably inflated by larger-than-normal cost-of-living changes which might not be absolutely picked up within the seasonal changes. This implies from the standpoint of inflation fears, the image might not be that dangerous. From the standpoint of employees seeing actual pay will increase, with wages outpacing inflation, it is extremely good.
Labor Market Nonetheless Very Robust
The January jobs information have been robust by virtually each measure. Whereas the financial system clearly can not go on including 500,000 jobs a month, it’s probably that a minimum of a part of the January beneficial properties was attributable to uncommon seasonal components that won’t be repeated.
It is usually considerably disconcerting that the family survey continues to indicate a really totally different image of the labor market. It isn’t uncommon for the surveys to be wildly out of sync for a month or two, and even longer, however the 2.2 million hole during the last 12 months between job development within the institution survey and employment development within the family survey is extraordinary. Most different information appear extra carefully aligned to information within the institution survey, however additional revisions might present a unique story.
